TDG for Corrosion Prevention
Thermal diffusion galvanizing (TDG aka TDZ) is an environmentally friendly method of protecting metals that offers superior corrosion and wear resistance along with uniform coating. TDG coatings are:
- Sacrificial
- Non-galling, similar to cadmium
- Strongly adhered to the surface due to diffusion of both iron and zinc
- Not susceptible to hydrogen embrittlement
- Environmentally friendly – the EPA describes TDG as near-zero discharge process and it won the most valuable pollution prevention technology award
- Made in the US (in our case at least!)
- Heat resistant
- Uniformly applied.
What is Thermal Diffusion Galvanizing?
While traditional hot-dip galvanizing (HDG) involves many steps and includes a dip in a bath that can leave uneven thicknesses and susceptibility to hydrogen embrittlement, TDG (also known as sherardizing) is a process that involves vapor deposition of zinc that creates a uniform layer even on threads and uneven surfaces. TDG improves the mechanical properties of coated materials at the same time as it enhances corrosion and wear resistance.
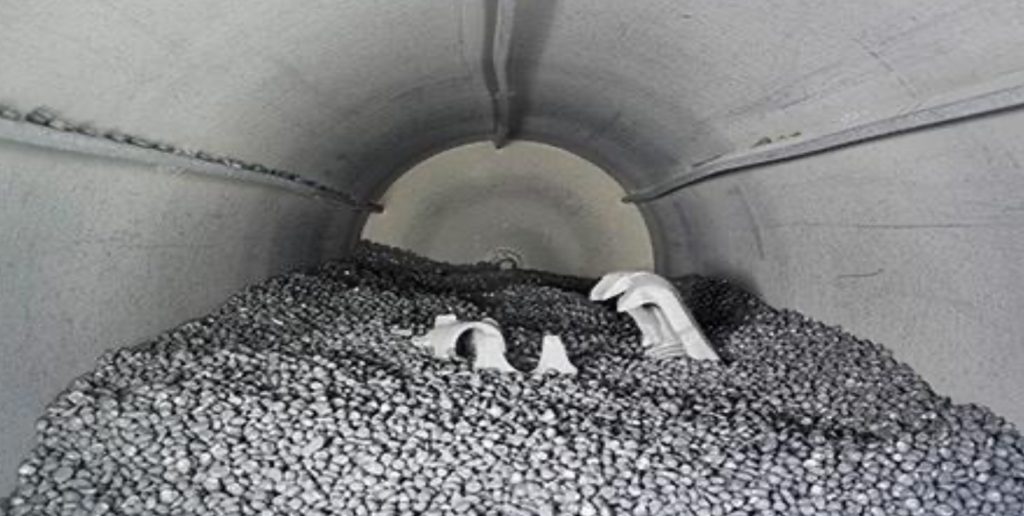
In TDG, samples are secured in an air-tight vessel filled with an inert gas and zinc powder, and then rotated slowly to expose all sides equally. The vessel is heated to just below the melting temperature of zinc, allowing the zinc to settle and diffuse on to the sample surface.
The samples are heated while surrounded by zinc that vaporizes and deposits over time. Longer applications result in thicker coatings:

What is the Corrosion Resistance go TDG Coatings?
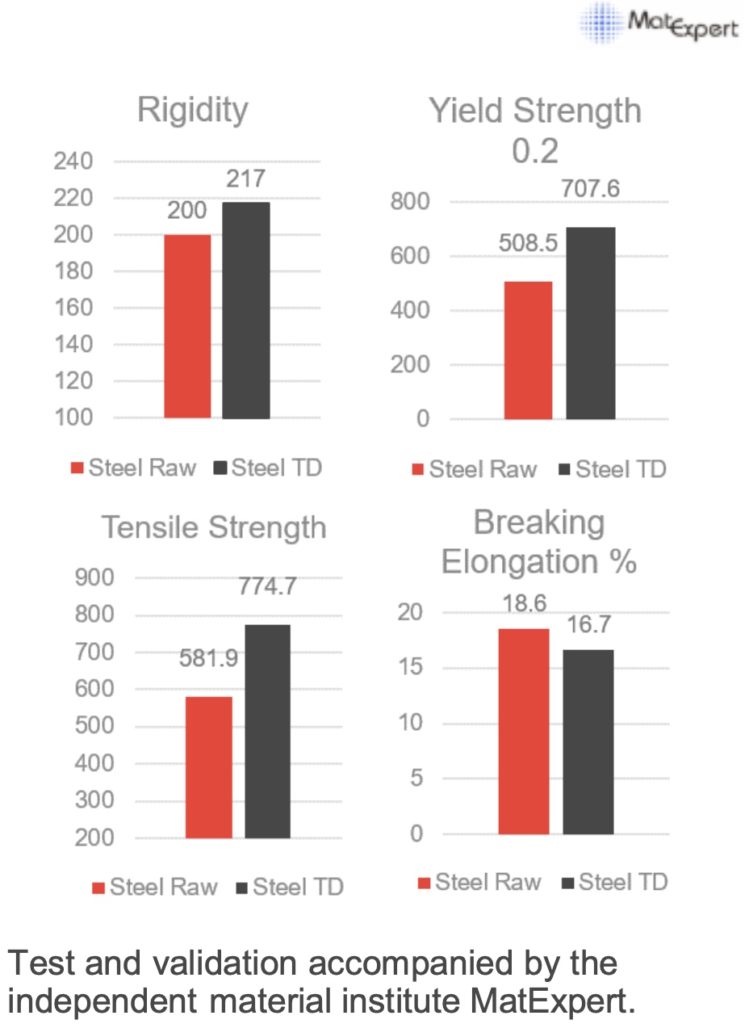
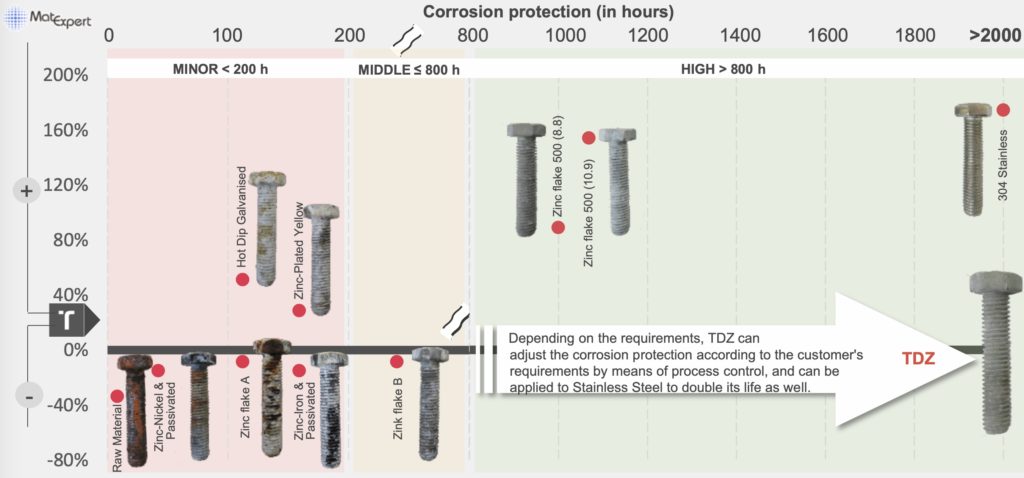
TDG (aka TDZ) coated parts exhibit thousands of hours of salt fog corrosion resistance, making them ideal for both storage (prior to use) and service in aggressive applications. The results below compare a variety of traditional zinc coatings with the TDZ (TDG) bolts:
How does TDG perform in bending?
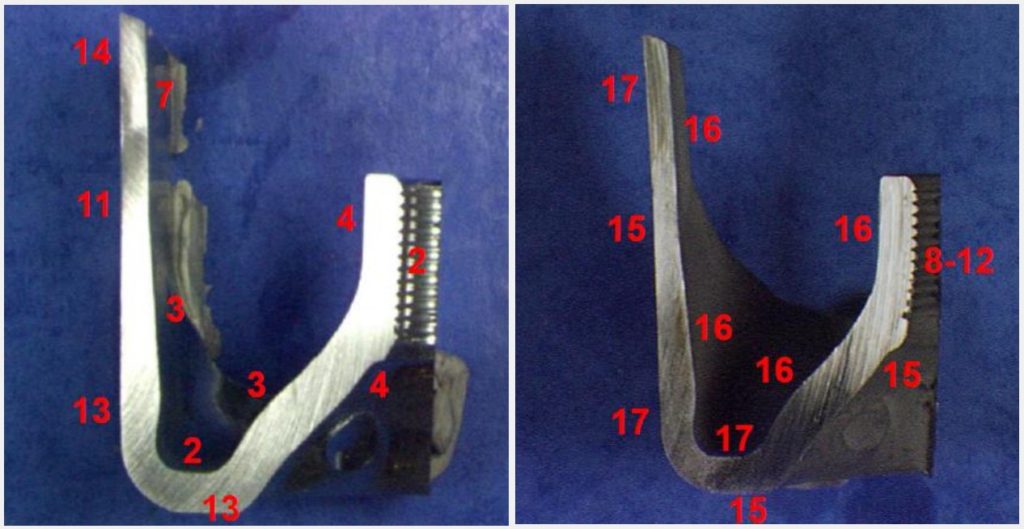
TDG has a strong metallurgical bond to the substrate because of the diffusion that occurs in both directions as the TDG is applied. Therefore, the mechanical performance in bending and distortion is excellent. The image below shows the apex of a TDG test sample bent 180 degrees around a 1″ mandrel. No cracking or distortion was observed:

How does TDG Galvanizing Compare with Hot Dip Galvanizing?
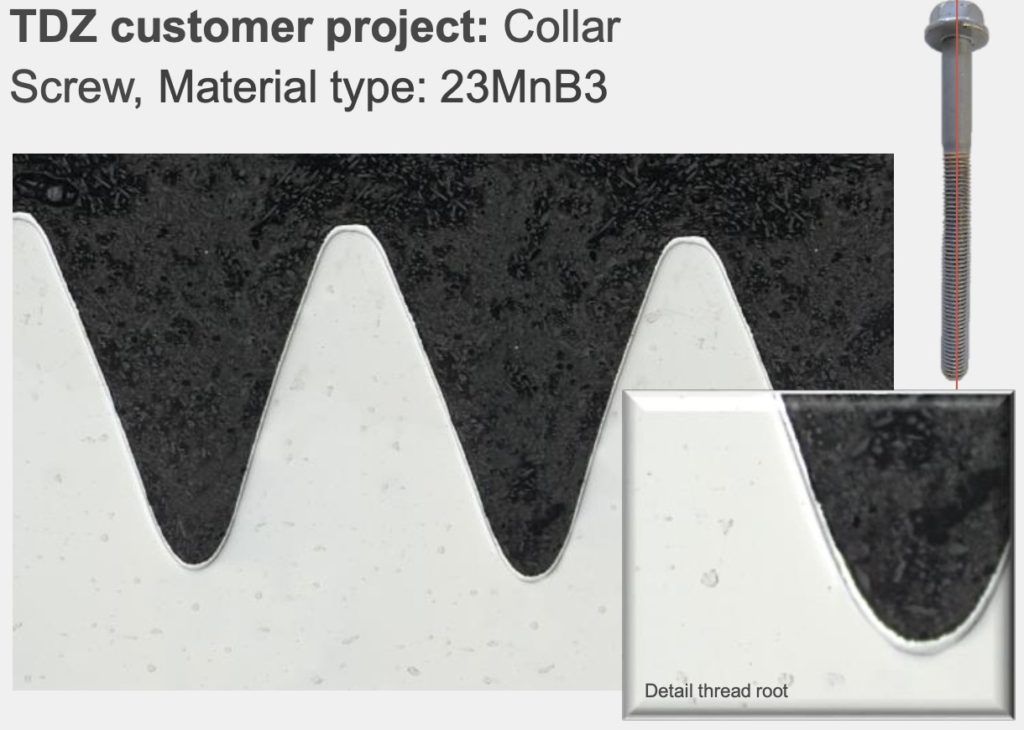
TDG has numerous advantages, including corrosion and wear resistance, and ability to resist hydrogen embrittlement. Furthermore, TDG is environmentally friendly and provides a much more uniform coated surface. The part on the left below was hot-dip galvanized and on the right is the thermally diffused zinc galvanized. The galvanized coating varies widely in thickness, barely covering the threads, while the TDZ coating is very uniform in thickness and covers the threads well.

Can TDG Galvanized Parts Experience Hydrogen Embrittlement?
Unlike HDG, TDG does not cause hydrogen embrittlement because it avoids the acid cleaning and other steps that can induce high levels of hydrogen and subsequent embrittlement. Furthermore, the high temperature of the process actually helps to further reduce the amount of hydrogen and reduces stress.
What is Wear Resistance of TDG Galvanization?
TDG galvanizing provides excellent adherence and wear resistance. In our laboratory tests, TDG can withstand abrasion, impact, and torque very well. With a low coefficient of friction and the ability to achieve hundreds of make or break tests (an aggressive test used in drilling evaluation to see how many times a component can survive being connected and disconnected. The excellent coverage of both the crest and root of the thread helps ensure the threads are sufficiently coated to mate effectively.

Where Can I Get TDG Galvanized Parts?
US Corrosion is a distributor of TDG galvanizing for materials of all shapes and sizes. Contact us for more info!